Decision No. 1313/2013/EU of the European Parliament and the Council on a Union Civil Protection Mechanism is basic EU document in the field of Civil Protection. This legislative tool provides closer cooperation of the Participating States and better coordination and reaction to disasters inside as well as outside of the EU. Its main aim is to support, coordinate and complement activities of the Participating States in the field of Civil Protection and to improve the effectiveness of systems in the field of prevention, preparedness and response to the natural and man-made disasters. Currently the Union Civil Protection Mechanism applies to 27 Member States of the EU, Montenegro, Iceland, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Türkiye, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Ukraine. The use of some of its measures is also made available to other candidate countries and potential candidates and countries that are part of the European Neighbourhood Policy.
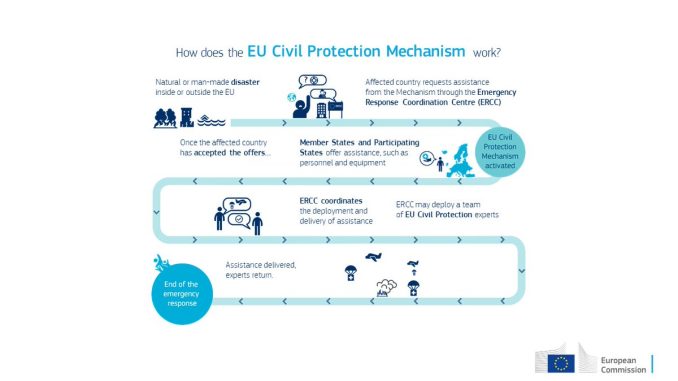
The Union Civil Protection Mechanism has a number of its own tools available to provide an assistance to affected State, if the assistance is requested. This includes, in particular, the Emergency Response Coordination Centre (ERCC) and the Common Emergency Communication and Information System (CECIS). Through these two tools it is possible to coordinate and communicate the requested and offered assistance while solving its transportation.
CECIS primarily links the relevant authorities and contact points in Participating States and the ERCC (in case of the Czech Republic, the contact point is national operational and information centre of DG FRS CR). It also contains databases with information about the registration and availability of Participating States' resources voluntarily allocated to disaster response. It also enables to communicate and disseminate the experience gained from civil protection interventions.
ERCC is fully operational 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Its key tasks are to:
- operate as EU Disaster Monitoring and Coordination Platform and as a communication centre for Participating States, affected states and field workers;
- develop and disseminate information products (daily information on disasters around the world, satellite maps, etc.);
- support coordination between civil protection operations and humanitarian aid operations.
In order to improve the planning of operations and to strengthen the availability of key resources, the Union Civil Protection Mechanism introduced the so-called European Emergency Response Capacities (EERC). The EERC are composed of Member States' voluntary resources and include civil protection modules, a number of specialized teams, expert advisory missions, material or supplies for relief needed to mitigate the immediate consequences of disasters (generators, water pumps, etc.).
The civil protection modules are currently considered as the main operative tool of the EERC. They are consisted of resources of one or number of Participating States and they are able to proceed predefined response tasks in accordance with established international guidelines, therefore they can:
- be deployed in very short term from the receiving the request of assistance through the ERCC;
- work individually and self-sufficiently for scheduled time period.
At the same time, these modules are able to cooperate with other Union bodies or with international organizations (especially the UN).
Currently the Czech Republic offers the yellow-highlighted modules through the Union Civil Protection Mechanism:
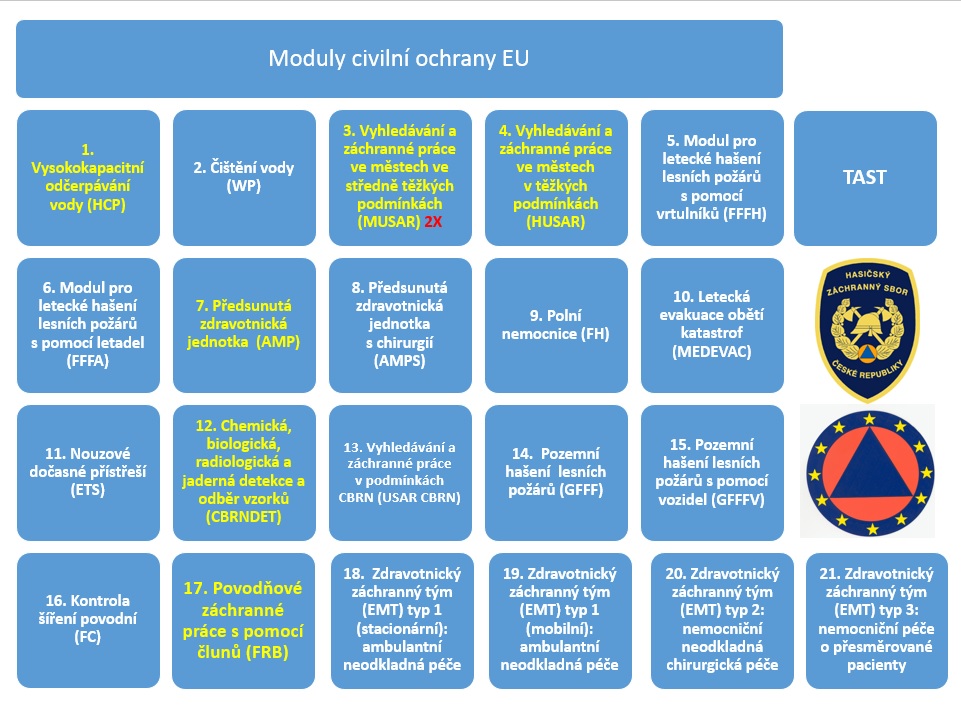
1. High capacity pumping (HCP) – Pumps water out of flooded areas, pumps water to help extinguish fires.
2. Water purification (WP) – Provides drinking water, performs water quality control
3. Medium urban search and rescue (MUSAR) – Searches for, locates and rescues victims who are under the rubble of collapsed houses, rescues people in traffic accidents and provides first aid
4. Heavy urban search and rescue (HUSAR) – Searches for, locates and rescues victims who are under the rubble of collapsed houses, rescues people in traffic accidents and provides first aid
5. Aerial forest firefighting module using helicopters (FFFH) – Performs aerial extinguishing of large forest fires and vegetation fires
6. Aerial forest fire fighting module using airplanes (FFFA) – Performs aerial extinguishing of large forest fires and vegetation fires
7. Advanced medical post (AMP) – Triages patients at the scene of the disaster, stabilizes their condition and prepares them for transport to the hospital
8. Advanced medical post with surgery module (AMPS) – Triages patients at the scene of the disaster, performs necessary life-saving surgical procedures, stabilizes their condition and prepares them for transport to the hospital
9. Field hospital module (FH) – Performs medical care
10. Medical aerial evacuation of disaster victims module (MEDEVAC) – Transports the injured to the hospital
11. Emergency temporary shelters (ETS) – Securing shelters and basic services until victims are taken over by local institutions or humanitarian organizations; includes tents with heating, electricity generators, sanitary facilities, drinking water supply, shelter for social activities
12. Chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear detection and sampling (CBRNDET), (chemical, biological, radiation or nuclear threats) – Records hazards, delineates contaminated areas, conducts sampling
13. Search and rescue in CBRN conditions (CBRN USAR) – Search and rescue work using special clothing
14. Ground forest fire fighting (GFFF) – Contributes to the extinguishing of large forest fires by ground vehicles
15. Ground forest fire fighting using vehicles (GFFF-V) – Contributes to extinguishing large forest fires and brush fires with the help of vehicles
16. Flood containment (FC) – Strengthens existing facilities and builds new barriers to prevent flooding from rising rivers, reservoirs and waterways
17. Flood rescue using boats (FRB) – Conducts search and rescue operations in water and assists persons stranded in flooded areas with the help of boats. It provides life-saving assistance and covers basic needs as needed.
18. Emergency medical team (EMT) type 1 (fixed): ambulatory urgent care – Triage, assessment, first aid, stabilization and redirection of serious emergency cases, definitive care in less serious emergency cases (traumatic and non-traumatic)
19. Emergency medical team (EMT) type 1 (mobile): ambulatory urgent care – Triage, assessment, first aid, stabilization and redirection of serious emergency cases, definitive care in less serious emergency cases (traumatic and non-traumatic)
20. Emergency medical team (EMT) type 2: hospital emergency surgical care – Acute hospital care, general and obstetric surgery in case of trauma and other serious illnesses
21. Emergency medical team (EMT) type 3: comprehensive hospital surgical care for patients including capacity for intensive care
Links
[Decision of the European Parliament 2019_03_20]
[Prováděcí pravidla k mechanismu civilní ochrany Unie 2014_11_06]
[Prováděcí pravidla k Rozhodnutí Evropského Parlamentu 2018_01_30]
